Lab 2: Implementation of ANN in R
In this lab, we will learn how to implement neural network models using Keras package in the R environment. At the same time, these examples will provide varying degrees of support for the discussions in the lecture notes.
Keras: A High-Level Deep Learning API
With the rise of deep learning, frameworks like TensorFlow provide powerful tools for building neural networks. However, working directly with these low-level libraries can be complex. Keras simplifies this process by offering a high-level API, making it easier to define and train deep learning models. While Python users can directly use Keras, R users may find it less accessible. The keras R package solves this problem by providing an R interface to Keras, allowing R users to build and train deep learning models seamlessly within the R environment.
The key feature of Keras is its modular design for deep learning architectures. For example, in a typical neural network model, Keras treats each layer as a dense unit.
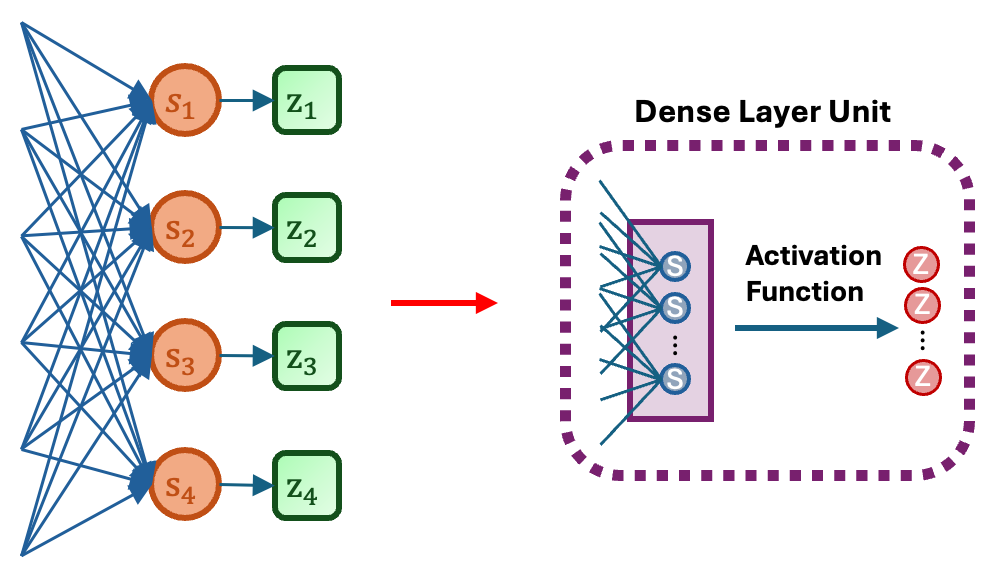
For such a dense layer unit, we can represent it using the function layer_dense. The details of this dense layer unit can be specified by different augments
layer_dense(units = 256, # the number of resulting neurons Z
activation = "relu", # the activation function
input_shape = c(784)) # one can specify the input shape when it is the first hidden layerThere are many other such modules, such as:
layer_dropout– Dropout regularization layerlayer_conv_2d– 2D Convolutional layer
layer_max_pooling_2d– 2D Max Pooling layer
layer_batch_normalization– Batch Normalization layer
These modules can be combined to build various deep learning models, such as fully connected neural networks (DNNs), convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
Keras Installation
Installing the Keras package in the R environment can be either easy or complex, depending on your computer. However, it doesn’t mean that the newer your computer is, the easier it will be. Therefore, I suggest you try installing the Keras package and the backend language, such as TensorFlow, on your computer first. If you can install it successfully, that’s great. However, if you encounter issues, I recommend using cloud-based R computing resources to install and learn.
For cloud-based R computing resources, you can use R Posit Cloud, which provides an easy-to-use platform for running R code and installing packages like Keras and TensorFlow without the need to set up complex local environments. By using R Posit Cloud, you can bypass the limitations of your local machine and access powerful computational resources, making it an ideal option for installing and learning deep learning with R.
For detailed installation methods, please refer to this online tutorial. Keras Tensorflow installation in R
Keras 4-step Method
As I mentioned before, Keras provides a great high-level API for deep learning. I summarized the implmentation process as the Keras 4-step method.
Next, let’s learn the four-step method based on the specific problem. You will have four tasks. First, we will go through the four-step method in detail by estimating linear regression using Keras. Then, in Task 2, we will modify the program to create a logistic regression classifier trained with Keras. In Task 3, we will attempt to train a deep neural network model on high-resolution image data. Finally, in Task 4, we will learn more about Keras features through a simple ANN example.
